The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections
Biofilms are densely packed communities of microbial cells that grow on living or inert surfaces and surround themselves with secreted polymers. Many bacterial species form biofilms, and their study has revealed them to be complex and diverse. The structural and physiological complexity of biofilms has led to the idea that they are coordinated and cooperative groups, analogous to multicellular organisms.1)
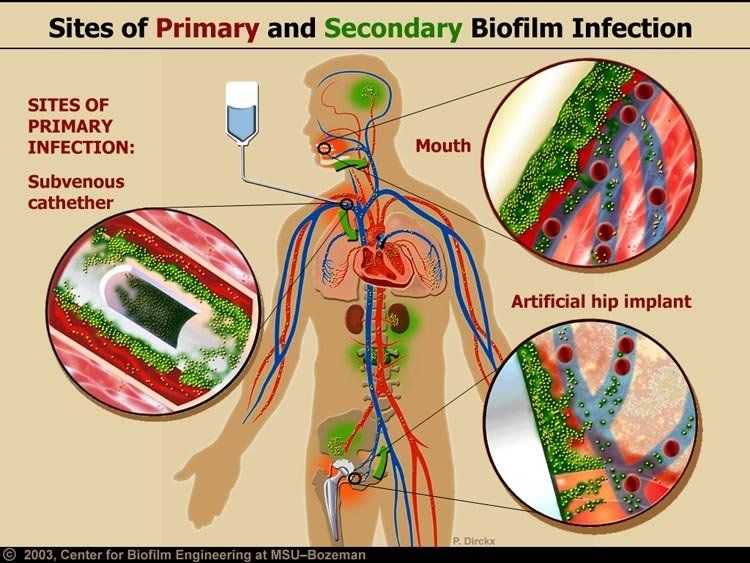
Researchers have estimated that 60-80 per cent of microbial infections in the body are caused by bacteria growing as a biofilm – as opposed to planktonic (free-floating) bacteria.
Researchers have estimated that 60-80 per cent of microbial infections in the body are caused by bacteria growing as a biofilm – as opposed to planktonic (free-floating) bacteria.
- There is a perception that single-celled organisms are asocial, but that is misguided. When bacteria are under stress—which is the story of their lives—they team up and form this collective called a biofilm. If you look at naturally occurring biofilms, they have very complicated architecture. They are like cities with channels for nutrients to go in and waste to go out.
Andre Levchenko, PhD, Johns Hopkins University
Some external biofilm, namely chronic wounds and dental plaque, can be manually removed. Because of their inaccessibility and heightened resistance to certain antibiotic combinations and dosages, internal biofilm is more difficult to eradicate.
Biofilm bacteria are a part of what is known as the Th1 bacterial pathogens, which collectively cause chronic disease.
Biofilm bacteria are a part of what is known as the Th1 bacterial pathogens, which collectively cause chronic disease.
History of biofilm research
Perhaps because many biofilms are thick enough to be visible to the naked eye, the microbial communities were among the first to be studied by early microbiologists. Anton van Leeuwenhoek scraped the plaque biofilm from his teeth and observed what he described as the "animalcules" inside them under his primitive microscope.
In the years which followed, researchers have concentrated primarily on planktonic (free-floating) bacteria, the kinds of microbes studied by the likes of Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch. It was not until the 1970s that scientists began to appreciate that bacteria in the biofilm mode of existence constitute such a major component of the bacterial biomass in most environments. In the 1980s and 1990s, scientists began to understand how elaborately organized a bacterial biofilm community can be.3)
Paul Stoodley of the Center for Biofilm Engineering at Montana State University attributes much of the lag in studying biofilms to the difficulties of working with heterogeneous biofilms compared with homogeneous planktonic populations. In a 2004 paper in Nature Reviews, the molecular biologist describes many reasons why biofilms are extremely difficult to culture, such as the fact that the diffusion of liquid through a biofilm and the fluid forces acting on a biofilm must be carefully calculated if it is to be cultured correctly. According to Stoodley, the need to master such difficult laboratory techniques has deterred many scientists from attempting to work with biofilms.4)
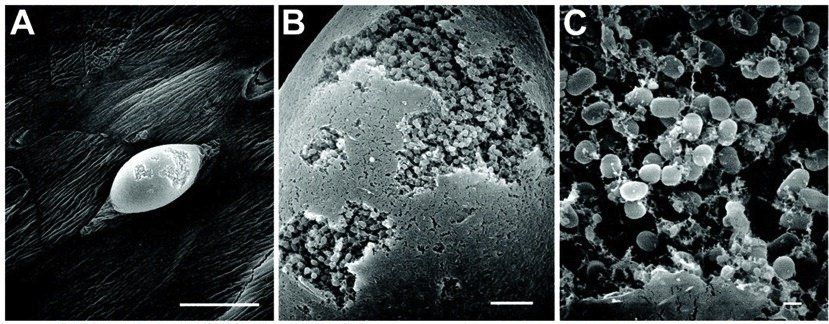
Although research on biofilms has surged in the last 20-30 years, the majority of biofilm research to date has focused on external biofilms or those that form on various surfaces in our natural environment. Better tools to analyze external biofilms has realized they cause a wide range of problems in industrial environments. For example, biofilms can develop on the interiors of pipes, which can lead to clogging and corrosion. Biofilms on floors and counters can make sanitation difficult in food preparation areas.
Since biofilms have the ability to clog pipes, watersheds, storage areas, and contaminate food products, large companies with facilities that are negatively impacted by their presence have naturally taken an interest in supporting biofilm research, particularly research that specifies how biofilms can be eliminated.
This means that many recent advances in biofilm detection have resulted from collaborations between microbial ecologists, environmental engineers, and mathematicians. This research has generated new analytical tools that help scientists identify biofilms.
Prevalence of biofilm
According to a recent public statement from the National Institutes of Health, more than 65% of all microbial infections are caused by biofilms…. If one recalls that such common diseases as urinary tract infections (caused by E. coli and other pathogens), catheter infections (caused by Staphylococcus aureus and other gram-positive pathogens), child middle-ear infections (caused by Haemophilus influenzae, for example), common dental plaque formation, and gingivitis, all of which are caused by biofilms, are hard to treat or frequently relapsing, this figure appears realistic.
Kim Lewis 5)
Kim Lewis 5)
Diseases for which biofilm have been implicated
In just a short period of time, researchers studying internal biofilms have already determined they cause a number of chronic infections and diseases. Notable diseases include:
Atherosclerosis
– Biofilm may contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. Ott et al. 's work showed a diverse group of bacterial "signatures" in atherosclerotic lesions of patients with coronary heart disease.6) In a commentary following Ott's paper, Katz and Shannon concluded that his work suggested that atherosclerotic plaques are composed of "functional biofilm." The team noted that the characteristics of a "mature" arterial wall make it well-suited for biofilm formation and explains the inefficacy of antibiotics, such as macrolides or fluoroquinolones, in clinical trials.7)
Chronic sinusitis
– One study found that biofilms are present on the removed tissue of two-thirds of patients undergoing surgery for chronic inflammation of the sinuses.8)
Chronic wounds
– Biofilm have been implicated in chronic wounds. Dr Randall Wolcott has published work offering strategies for managing wounds.9)
Molecular analyses of chronic wound specimens revealed diverse polymicrobial communities and the presence of bacteria, including strictly anaerobic bacteria, not revealed by culture. Bacterial biofilm prevalence in specimens from chronic wounds relative to acute wounds observed in this study provides evidence that biofilms may be abundant in chronic wounds.
GA James et al. 10)
Cystic fibrosis – The lungs of individuals with cystic fibrosis are colonized and infected by bacteria from an early age. These bacteria, which often spread amongst individuals with CF, thrive in the altered mucus, which collects in the small airways of the lungs. Over time, both the types of bacteria and their individual characteristics change in individuals with CF. In the initial stage, common bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Hemophilus influenzae colonize and infect the lungs. Eventually, however, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (and sometimes Burkholderia cepacia) dominates. Once within the lungs, these bacteria adapt to the environment and develop resistance to commonly used antibiotics. Pseudomonas can develop unique characteristics that allow the formation of large colonies, known as "mucoid" Pseudomonas, which are rarely seen in people that do not have cystic fibrosis.11) Infection by the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality among patients with cystic fibrosis.12)
GA James et al. 10)
Cystic fibrosis – The lungs of individuals with cystic fibrosis are colonized and infected by bacteria from an early age. These bacteria, which often spread amongst individuals with CF, thrive in the altered mucus, which collects in the small airways of the lungs. Over time, both the types of bacteria and their individual characteristics change in individuals with CF. In the initial stage, common bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Hemophilus influenzae colonize and infect the lungs. Eventually, however, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (and sometimes Burkholderia cepacia) dominates. Once within the lungs, these bacteria adapt to the environment and develop resistance to commonly used antibiotics. Pseudomonas can develop unique characteristics that allow the formation of large colonies, known as "mucoid" Pseudomonas, which are rarely seen in people that do not have cystic fibrosis.11) Infection by the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality among patients with cystic fibrosis.12)
Endocarditis
– Inflammation of the smooth membranes which line the inside of the heart is caused by a complex biofilm composed of both bacterial and host components.13)
Inner ear infections
– The majority of ear infections are caused by biofilm bacteria.14) These infections, which can be either acute or chronic, are referred to collectively as otitis media (OM). They are the most common illness for which children visit a physician, receive antibiotics, or undergo surgery in the United States.
It appears that in many cases recurrent disease stems not from re-infection as was previously thought and which forms the basis for conventional treatment, but from a persistent biofilm…. [The discovery of biofilms in the setting of chronic otitis media represents] a landmark evolution in the medical community's understanding about a disease that afflicts millions of children worldwide each year and further endorses the emerging biofilm paradigm of chronic infectious disease.
Garth Ehrlich, PhD
Garth Ehrlich, PhD
Kidney stones
– Biofilms also cause the formation of kidney stones.15) The stones cause symptoms of the disease by obstructing urine flow and by producing inflammation and recurrent infection that can lead to kidney failure. Approximately 15%–20% of kidney stones occur in the setting of urinary tract infection. According to Matthew Parsek, PhD, these stones are produced by the interplay between infecting bacteria and mineral substrates derived from the urine. This interaction results in a complex biofilm composed of bacteria, bacterial exoproducts, and mineralized stone material.
Leptospirosis
– Biofilms also cause leptospirosis, a severe but neglected emerging disease that infects humans through contaminated water. Previously, scientists believed the bacteria associated with leptospirosis were planktonic (free-floating). One research team has shown that Leptospira interrogans can make biofilms, which could be one of the main factors controlling survival and disease transmission.16) According to the study's author, 90% of the species of Leptospira tested could form biofilms, and it takes L. interrogans an average of 20 days to make a biofilm.
Osteomyelitis
– According to Parsek, biofilms may also cause osteomyelitis, a disease in which the bones and bone marrow become infected. This is supported by the fact that microscopy studies have shown biofilm formation on infected bone surfaces from humans and experimental animal models.17)
osteonecrosis and osteomyelitis of the jaw – Of 20 patients with these bone disease, all "exhibited large surface areas of bone occluded with well-developed biofilms." 18)
Periodontal disease – Perhaps the most well-known and studied biofilm bacteria. Hundreds of microbial biofilm colonize the human mouth, causing tooth decay and gum disease.
osteonecrosis and osteomyelitis of the jaw – Of 20 patients with these bone disease, all "exhibited large surface areas of bone occluded with well-developed biofilms." 18)
Periodontal disease – Perhaps the most well-known and studied biofilm bacteria. Hundreds of microbial biofilm colonize the human mouth, causing tooth decay and gum disease.
Plaque is a biofilm on the surfaces of the teeth. This accumulation of microorganisms subject the teeth and gingival tissues to high concentrations of bacterial metabolites which results in dental disease.
Matthew Parsek, PhD 19)
Matthew Parsek, PhD 19)
Dental plaque is composed of more than 500 species.20)
Prosthetic joints and heart valves
– Pathogenic biofilms are also commonly found on medical devices such as joint prostheses and heart valves.21) Dr Patel of the Mayo Clinic has concluded that prosthetic joints increase the likelihood of biofilm infection.
When people think of infection, they may think of fever or pus coming out of a wound. However, this is not the case with prosthetic joint infection. Patients will often experience pain, but not other symptoms usually associated with infection. Often what happens is that the bacteria that cause infection on prosthetic joints are the same as bacteria that live harmlessly on our skin. However, on a prosthetic joint, they can stick, grow and cause problems over the long term. Many of these bacteria would not infect the joint were it not for the prosthesis.
Robin Patel, MD, EurekaAlert!
When people think of infection, they may think of fever or pus coming out of a wound. However, this is not the case with prosthetic joint infection. Patients will often experience pain, but not other symptoms usually associated with infection. Often what happens is that the bacteria that cause infection on prosthetic joints are the same as bacteria that live harmlessly on our skin. However, on a prosthetic joint, they can stick, grow and cause problems over the long term. Many of these bacteria would not infect the joint were it not for the prosthesis.
Robin Patel, MD, EurekaAlert!
Urinary tract infections
– In their 2003 Science paper, Anderson et al. reported that in the case of UTIs, intracellular Escherichia coli can mature into biofilms, creating pod-like bulges on the bladder surface. Explains how bladder infections can persist in the face of robust host defences.22) "The idea that biofilms might form inside human cells is really novel," said internist Pradeep Singh of the University of Iowa College of Medicine in Iowa City, who studies lung biofilms that plague children with cystic fibrosis.
Veterinary diseases
– Biofilms have also been implicated in a wide array of veterinary diseases.23)
The life cycle of biofilm communities
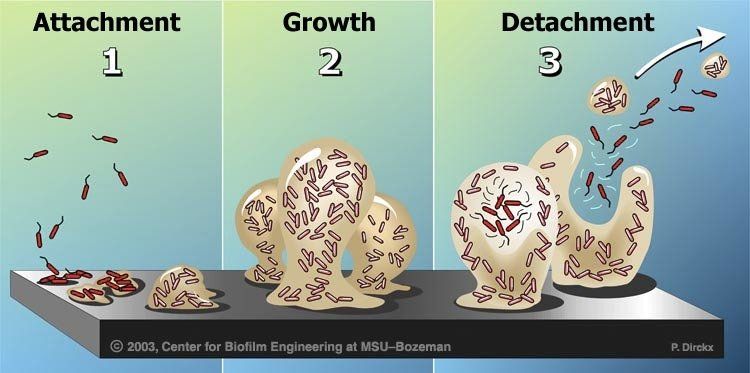
Attachment/colonization
Biofilms form when bacteria adhere to surfaces in aqueous environments and begin to excrete a slimy, glue-like substance that can anchor them to a variety of materials including metals, plastics, soil particles, medical implant materials and, most significantly, human or animal tissue. The first bacterial colonists to adhere to a surface initially do so by inducing weak, reversible bonds called van der Waals forces. If the colonists are not immediately separated from the surface, they can anchor themselves more permanently using cell adhesion molecules, proteins on their surfaces that bind other cells in a process called cell adhesion.
These bacterial pioneers facilitate the arrival of other pathogens by providing more diverse adhesion sites. They also begin to build the matrix that holds the biofilm together. If there are species that are unable to attach to a surface on their own, they are often able to anchor themselves to the matrix or directly to earlier colonists. The expression of 800 genes have been shown to be altered when a single bacterial species join a biofilm.25)
According to Costerton, the genes that allow a biofilm to develop are activated after enough cells attach to a solid surface.
It appears that attachment itself is what stimulates the synthesis of the extracellular matrix in which the sessile bacteria are embedded. This notion– that bacteria have a sense of touch that enables detection of a surface and the expression of specific genes is in itself an exciting area of research.
William Costerton et al. 26)
It appears that attachment itself is what stimulates the synthesis of the extracellular matrix in which the sessile bacteria are embedded. This notion– that bacteria have a sense of touch that enables detection of a surface and the expression of specific genes is in itself an exciting area of research.
William Costerton et al. 26)
Research on the molecular and genetic basis of biofilm development has shown that when cells switch from planktonic to community mode, they also undergo a shift in behaviour that involves alterations in the activity of numerous genes. There is evidence that specific genes must be transcribed during the attachment phase of biofilm development. In many cases, the activation of these genes is required for the synthesis of the extracellular matrix that protects the pathogens inside.
Growth and development
After the initial colonization, the biofilm grows through a combination of cell division and recruitment. The next stage of biofilm formation is known as development and is the stage in which the biofilm is established and may only change in shape and size.
Once a biofilm has more fully formed, it often contains channels in which nutrients can circulate. Cells in different regions of a biofilm also exhibit different patterns of gene expression. Because biofilms often develop their own metabolism, they are sometimes compared to the tissues of higher organisms, in which closely packed cells work together and create a network in which minerals can flow.
Biofilms grow slowly, in diverse locations, and biofilm infections are often slow to produce overt symptoms.
Movement
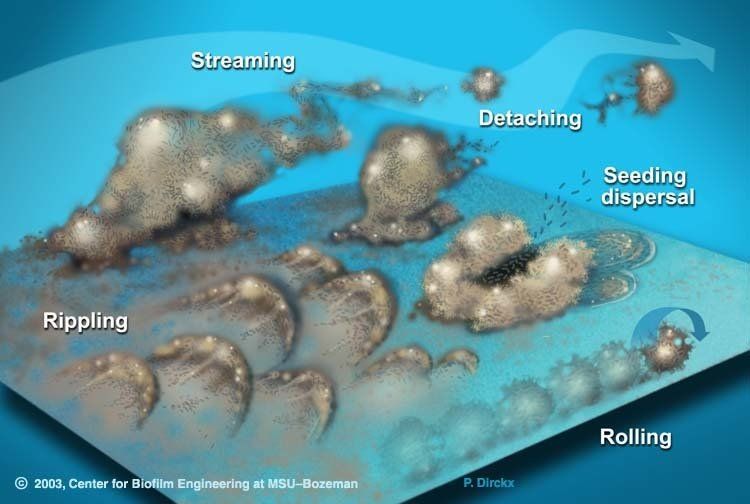
Biofilm bacteria can move in numerous ways that allow them to infect new tissues easily. Biofilms may move collectively, by rippling or rolling across the surface, or by detaching in clumps. Sometimes, in a dispersal strategy referred to as "swarming/seeding", a biofilm colony differentiates to form an outer "wall" of stationary bacteria, while the inner region of the biofilm "liquefies", allowing planktonic cells to "swim" out of the biofilm and leave behind a hollow mound.27)
Detachment and external colonization
Researchers often note that, once biofilms are established, planktonic bacteria may periodically leave the biofilm on their own. When they do, they can rapidly multiply and disperse. There is a natural pattern of a programmed detachment of planktonic cells from biofilms. This means that biofilms can act as what Costerton refers to as "niduses" of acute infection. Because the bacteria in a biofilm are protected by a matrix, the host immune system is less likely to mount a response to their presence.28)
But if planktonic bacteria are periodically released from the biofilms, each time single bacterial forms enter the tissues; the immune system suddenly becomes aware of their presence. It may proceed to mount an inflammatory response that leads to heightened disease symptoms. Thus, the periodic release of planktonic bacteria from some biofilms may be what causes many chronic relapsing infections.
As Matthew R. Parsek of Northwestern University describes in a 2003 paper in the Annual Review of Microbiology, any pathogen that survives in a chronic form benefits by keeping the host alive.29) After all, if a chronic bacterial form kills its host, it will no longer have a place to live. So according to Parsek, chronic infection often results in a "disease stalemate" where bacteria of moderate virulence are somewhat contained by the defences of the host. The infectious agents never actually kill the host, but the host is never able to kill the invading pathogens either entirely.
As Matthew R. Parsek of Northwestern University describes in a 2003 paper in the Annual Review of Microbiology, any pathogen that survives in a chronic form benefits by keeping the host alive.29) After all, if a chronic bacterial form kills its host, it will no longer have a place to live. So according to Parsek, chronic infection often results in a "disease stalemate" where bacteria of moderate virulence are somewhat contained by the defences of the host. The infectious agents never actually kill the host, but the host is never able to kill the invading pathogens either entirely.
Parsek believes that the optimal way for bacteria to survive under such circumstances is in a biofilm, stating that "Increasing evidence suggests that the biofilm mode of growth may play a key role in both of these adaptations. Biofilm growth increases the resistance of bacteria to killing and may make organisms less conspicuous to the immune system…. ultimately this moderation of virulence may serve the bacteria's interest by increasing the longevity of the host."
Advantages of biofilm
Biofilm communities provide several advantages to their members, including easy access to food and nutrients and resistance to antibiotics.
Biofilm communities provide several advantages to their members, including easy access to food and nutrients and resistance to antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistance
This development of a biofilm allows for the cells inside to become more resistant to the body's natural antimicrobials as well as the antibiotics administered in a standard fashion. In fact, depending on the organism and antimicrobial and experimental system, biofilm bacteria can be up to a thousand times more resistant to antimicrobial stress than free-swimming bacteria of the same species.
Ability to enter into latent states during inhospitable conditions
In the midst of inhospitable conditions such as nutrient starvation, microbes in biofilm communities can enter into a viable but nonculturable state.30) According to Epstein,31) members of microbial communities periodically wake up from this state of dormancy. In a method analogous to "sending out scouts" to "test the environment" for its suitability for growth of the entire population. In this scenario, if the resuscitating cells "detect" that the previously stressful/adverse environment is now growth-permissive, they would signal the remaining cells to resuscitate.32)
Freeloaders
Even though a biofilm tends to benefit all its members, understanding how such cooperation among pathogens evolves and is maintained may represent one of evolutionary biology's thorniest problems. Biofilm bacteria appear to resolve the issue of freeloaders in at least two ways:
Increasing species diversity – Once inside a biofilm, P. fluorescens, for example, differentiates into various forms, each of which uses different nutrient resources. The fact that these "diverse cooperators" don't all compete for the same chemicals and nutrients substantially reduces competition for resources within the biofilm.33)
Disbanding when there are too many freeloaders
A study of a cultured E. coli colony (not necessarily in a biofilm state) found that individual microbes can act altruistically through a form of kin selection.34) Essentially, they sacrifice themselves so that their fellow bacteria have a better chance at survival.
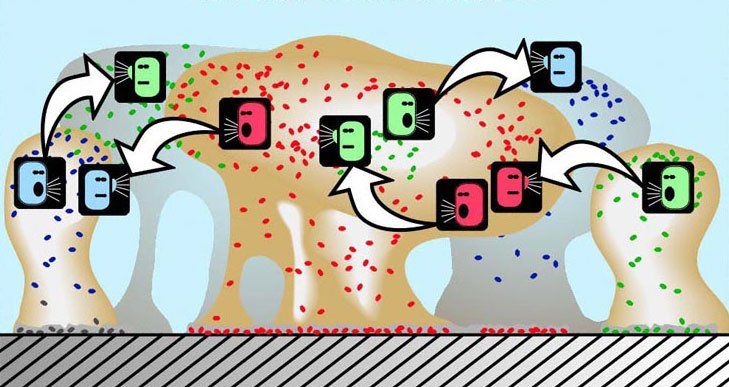
Quorum sensing
The bacteria that become part of a biofilm engage in quorum sensing, a type of decision-making process in which behaviour is coordinated through a "chemical vocabulary." 35) Although the mechanisms behind quorum sensing are not fully understood, the communication process allows, for example, a single-celled bacterium to perceive how many other bacteria are in close proximity. If a bacterium can sense that it is surrounded by a dense population of other pathogens, it is more inclined to join them and contribute to the formation of a biofilm.
Quorum sensing can occur within a single bacterial species as well as between diverse species and can regulate a host of different processes, primarily serving as a simple communication network. A variety of different molecules can be used as signals.
For example, researchers at the University of Iowa (several of whom are now at the University of Washington) have spent the last decade identifying the molecules that allow the bacterial species P. aeruginosa to form biofilms in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis.36)
Singh and his colleagues finally discovered that P. aeruginosa uses one of two particular quorum-sensing molecules to initiate the formation of biofilms. In November 1999, his research team screened the entire bacterial genome, identifying 39 genes that are strongly controlled by the quorum-sensing system.
In a 2000 study published in Nature, Singh and colleagues developed a sensitive test which shows P. aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis lungs produces the telltale, quorum-sensing molecules that are the signals for biofilm formation.37)
References
1)The sociobiology of biofilms.
Nadell CD, Xavier JB, Foster KR
FEMS Microbiol Rev33p206-24(2009 Jan)
2)Biofilm-related disease.
Del Pozo JL
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther16p51-65(2018 Jan)
3) , 26) , 28)Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections.
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP
Science284p1318-22(1999 May 21)
4)Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases.
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P
Nat Rev Microbiol2p95-108(2004 Feb)
5)Riddle of biofilm resistance.
Lewis K
Antimicrob Agents Chemother45p999-1007(2001 Apr)
6)Detection of diverse bacterial signatures in atherosclerotic lesions of patients with coronary heart disease.
Ott SJ, El Mokhtari NE, Musfeldt M, Hellmig S, Freitag S, Rehman A, Kühbacher T, Nikolaus S, Namsolleck P, Blaut M, Hampe J, Sahly H, Reinecke A, Haake N, Günther R, Krüger D, Lins M, Herrmann G, Fölsch UR, Simon R, Schreiber S
Circulation113p929-37(2006 Feb 21)
7)Bacteria and coronary atheroma: more fingerprints but no smoking gun.
Katz JT, Shannon RP
Circulation113p920-2(2006 Feb 21)
8)Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with an unfavorable evolution after surgery for chronic sinusitis and nasal polyposis.
Bendouah Z, Barbeau J, Hamad WA, Desrosiers M
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg134p991-6(2006 Jun)
9)Regular debridement is the main tool for maintaining a healthy wound bed in most chronic wounds.
Wolcott RD, Kennedy JP, Dowd SE
J Wound Care18p54-6(2009 Feb)
10)Biofilms in chronic wounds.
James GA, Swogger E, Wolcott R, Pulcini E, Secor P, Sestrich J, Costerton JW, Stewart PS
Wound Repair Regen16p37-44(2008 Jan-Feb)
11)Microbiology of early CF lung disease.
Saiman L
Paediatr Respir Rev5 Suppl ApS367-9(2004)
12)Pseudomonal infection in cystic fibrosis: the battle continues.
Elkin S, Geddes D
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther1p609-18(2003 Dec)
13)Biofilm formation by enterococci.
Mohamed JA, Huang DB
J Med Microbiol56p1581-8(2007 Dec)
14) , 39)Direct detection of bacterial biofilms on the middle-ear mucosa of children with chronic otitis media.
Hall-Stoodley L, Hu FZ, Gieseke A, Nistico L, Nguyen D, Hayes J, Forbes M, Greenberg DP, Dice B, Burrows A, Wackym PA, Stoodley P, Post JC, Ehrlich GD, Kerschner JE
JAMA296p202-11(2006 Jul 12)
15) , 17) , 19) , 29)Bacterial biofilms: an emerging link to disease pathogenesis.
Parsek MR, Singh PK
Annu Rev Microbiol57p677-701(2003)
16)Biofilm formation by saprophytic and pathogenic leptospires.
Ristow P, Bourhy P, Kerneis S, Schmitt C, Prevost MC, Lilenbaum W, Picardeau M
Microbiology154p1309-17(2008 May)
18)Microbial biofilms in osteomyelitis of the jaw and osteonecrosis of the jaw secondary to bisphosphonate therapy.
Sedghizadeh PP, Kumar SK, Gorur A, Schaudinn C, Shuler CF, Costerton JW
J Am Dent Assoc140p1259-65(2009 Oct)
20)Dental plaque formation.
Rosan B, Lamont RJ
Microbes Infect2p1599-607(2000 Nov)
21)Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection.
Trampuz A, Piper KE, Jacobson MJ, Hanssen AD, Unni KK, Osmon DR, Mandrekar JN, Cockerill FR, Steckelberg JM, Greenleaf JF, Patel R
N Engl J Med357p654-63(2007 Aug 16)
22)Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections.
Anderson GG, Palermo JJ, Schilling JD, Roth R, Heuser J, Hultgren SJ
Science301p105-7(2003 Jul 4)
23)Biofilms and their relevance to veterinary medicine.
Clutterbuck AL, Woods EJ, Knottenbelt DC, Clegg PD, Cochrane CA, Percival SL
Vet Microbiol121p1-17(2007 Mar 31)
24)Biofilms in drinking water and their role as reservoir for pathogens.
Wingender J, Flemming HC
Int J Hyg Environ Healthp(2011 Jun 20)
25)Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm.
Sauer K, Camper AK, Ehrlich GD, Costerton JW, Davies DG
J Bacteriol184p1140-54(2002 Feb)
27)Clinical significance of seeding dispersal in biofilms.
Kirov SM, Webb JS, Kjelleberg S
Microbiology151p3452-3; discussion 3453(2005 Nov)
30) , 32)Recent findings on the viable but nonculturable state in pathogenic bacteria.
Oliver JD
FEMS Microbiol Rev34p415-25(2010 Jul)
31)Microbial awakenings.
Epstein SS
Nature457p1083(2009 Feb 26)
33)Character displacement promotes cooperation in bacterial biofilms.
Brockhurst MA, Hochberg ME, Bell T, Buckling A
Curr Biol16p2030-4(2006 Oct 24)
34)Bacterial charity work leads to population-wide resistance.
Lee HH, Molla MN, Cantor CR, Collins JJ
Nature467p82-5(2010 Sep 2)
35)The major Vibrio cholerae autoinducer and its role in virulence factor production.
Higgins DA, Pomianek ME, Kraml CM, Taylor RK, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL
Nature450p883-6(2007 Dec 6)
36) , 37)Quorum-sensing signals indicate that cystic fibrosis lungs are infected with bacterial biofilms.
Singh PK, Schaefer AL, Parsek MR, Moninger TO, Welsh MJ, Greenberg EP
Nature407p762-4(2000 Oct 12)
38)Natural and synthetic cathelicidin peptides with anti-microbial and anti-biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus.
Dean SN, Bishop BM, van Hoek ML
BMC Microbiol11p114(2011 May 23)
40)Biofilms and chronic infections.
Wolcott RD, Ehrlich GD
JAMA299p2682-4(2008 Jun 11)
41)From Koch's postulates to biofilm theory. The lesson of Bill Costerton.
Ehrlich GD, Arciola CR
Int J Artif Organs35p695-9(2012 Oct)
42)There is a specific response to pH by isolates of Haemophilus influenzae and this has a direct influence on biofilm formation.
Ishak N, Tikhomirova A, Bent SJ, Ehrlich GD, Hu FZ, Kidd SP
BMC Microbiol14p47(2014 Feb 21)
43)Wound Biofilm: Current Perspectives and Strategies on Biofilm Disruption and Treatments
Snyder RJ, Bohn G, Hanft J, Harkless L, Kim P, Lavery L, Schultz G, Wolcott R
Wounds29pS1-S17(2017 Jun)
44)<i>Staphylococcus aureus</i> biofilm removal by targeting biofilm-associated extracellular proteins.
Shukla SK, Rao TS
Indian J Med Res146pS1-S8(2017 Jul)
https://mpkb.org/home/pathogenesis/microbiota/biofilm
1)The sociobiology of biofilms.
Nadell CD, Xavier JB, Foster KR
FEMS Microbiol Rev33p206-24(2009 Jan)
2)Biofilm-related disease.
Del Pozo JL
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther16p51-65(2018 Jan)
3) , 26) , 28)Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections.
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP
Science284p1318-22(1999 May 21)
4)Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases.
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P
Nat Rev Microbiol2p95-108(2004 Feb)
5)Riddle of biofilm resistance.
Lewis K
Antimicrob Agents Chemother45p999-1007(2001 Apr)
6)Detection of diverse bacterial signatures in atherosclerotic lesions of patients with coronary heart disease.
Ott SJ, El Mokhtari NE, Musfeldt M, Hellmig S, Freitag S, Rehman A, Kühbacher T, Nikolaus S, Namsolleck P, Blaut M, Hampe J, Sahly H, Reinecke A, Haake N, Günther R, Krüger D, Lins M, Herrmann G, Fölsch UR, Simon R, Schreiber S
Circulation113p929-37(2006 Feb 21)
7)Bacteria and coronary atheroma: more fingerprints but no smoking gun.
Katz JT, Shannon RP
Circulation113p920-2(2006 Feb 21)
8)Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with an unfavorable evolution after surgery for chronic sinusitis and nasal polyposis.
Bendouah Z, Barbeau J, Hamad WA, Desrosiers M
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg134p991-6(2006 Jun)
9)Regular debridement is the main tool for maintaining a healthy wound bed in most chronic wounds.
Wolcott RD, Kennedy JP, Dowd SE
J Wound Care18p54-6(2009 Feb)
10)Biofilms in chronic wounds.
James GA, Swogger E, Wolcott R, Pulcini E, Secor P, Sestrich J, Costerton JW, Stewart PS
Wound Repair Regen16p37-44(2008 Jan-Feb)
11)Microbiology of early CF lung disease.
Saiman L
Paediatr Respir Rev5 Suppl ApS367-9(2004)
12)Pseudomonal infection in cystic fibrosis: the battle continues.
Elkin S, Geddes D
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther1p609-18(2003 Dec)
13)Biofilm formation by enterococci.
Mohamed JA, Huang DB
J Med Microbiol56p1581-8(2007 Dec)
14) , 39)Direct detection of bacterial biofilms on the middle-ear mucosa of children with chronic otitis media.
Hall-Stoodley L, Hu FZ, Gieseke A, Nistico L, Nguyen D, Hayes J, Forbes M, Greenberg DP, Dice B, Burrows A, Wackym PA, Stoodley P, Post JC, Ehrlich GD, Kerschner JE
JAMA296p202-11(2006 Jul 12)
15) , 17) , 19) , 29)Bacterial biofilms: an emerging link to disease pathogenesis.
Parsek MR, Singh PK
Annu Rev Microbiol57p677-701(2003)
16)Biofilm formation by saprophytic and pathogenic leptospires.
Ristow P, Bourhy P, Kerneis S, Schmitt C, Prevost MC, Lilenbaum W, Picardeau M
Microbiology154p1309-17(2008 May)
18)Microbial biofilms in osteomyelitis of the jaw and osteonecrosis of the jaw secondary to bisphosphonate therapy.
Sedghizadeh PP, Kumar SK, Gorur A, Schaudinn C, Shuler CF, Costerton JW
J Am Dent Assoc140p1259-65(2009 Oct)
20)Dental plaque formation.
Rosan B, Lamont RJ
Microbes Infect2p1599-607(2000 Nov)
21)Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection.
Trampuz A, Piper KE, Jacobson MJ, Hanssen AD, Unni KK, Osmon DR, Mandrekar JN, Cockerill FR, Steckelberg JM, Greenleaf JF, Patel R
N Engl J Med357p654-63(2007 Aug 16)
22)Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections.
Anderson GG, Palermo JJ, Schilling JD, Roth R, Heuser J, Hultgren SJ
Science301p105-7(2003 Jul 4)
23)Biofilms and their relevance to veterinary medicine.
Clutterbuck AL, Woods EJ, Knottenbelt DC, Clegg PD, Cochrane CA, Percival SL
Vet Microbiol121p1-17(2007 Mar 31)
24)Biofilms in drinking water and their role as reservoir for pathogens.
Wingender J, Flemming HC
Int J Hyg Environ Healthp(2011 Jun 20)
25)Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm.
Sauer K, Camper AK, Ehrlich GD, Costerton JW, Davies DG
J Bacteriol184p1140-54(2002 Feb)
27)Clinical significance of seeding dispersal in biofilms.
Kirov SM, Webb JS, Kjelleberg S
Microbiology151p3452-3; discussion 3453(2005 Nov)
30) , 32)Recent findings on the viable but nonculturable state in pathogenic bacteria.
Oliver JD
FEMS Microbiol Rev34p415-25(2010 Jul)
31)Microbial awakenings.
Epstein SS
Nature457p1083(2009 Feb 26)
33)Character displacement promotes cooperation in bacterial biofilms.
Brockhurst MA, Hochberg ME, Bell T, Buckling A
Curr Biol16p2030-4(2006 Oct 24)
34)Bacterial charity work leads to population-wide resistance.
Lee HH, Molla MN, Cantor CR, Collins JJ
Nature467p82-5(2010 Sep 2)
35)The major Vibrio cholerae autoinducer and its role in virulence factor production.
Higgins DA, Pomianek ME, Kraml CM, Taylor RK, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL
Nature450p883-6(2007 Dec 6)
36) , 37)Quorum-sensing signals indicate that cystic fibrosis lungs are infected with bacterial biofilms.
Singh PK, Schaefer AL, Parsek MR, Moninger TO, Welsh MJ, Greenberg EP
Nature407p762-4(2000 Oct 12)
38)Natural and synthetic cathelicidin peptides with anti-microbial and anti-biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus.
Dean SN, Bishop BM, van Hoek ML
BMC Microbiol11p114(2011 May 23)
40)Biofilms and chronic infections.
Wolcott RD, Ehrlich GD
JAMA299p2682-4(2008 Jun 11)
41)From Koch's postulates to biofilm theory. The lesson of Bill Costerton.
Ehrlich GD, Arciola CR
Int J Artif Organs35p695-9(2012 Oct)
42)There is a specific response to pH by isolates of Haemophilus influenzae and this has a direct influence on biofilm formation.
Ishak N, Tikhomirova A, Bent SJ, Ehrlich GD, Hu FZ, Kidd SP
BMC Microbiol14p47(2014 Feb 21)
43)Wound Biofilm: Current Perspectives and Strategies on Biofilm Disruption and Treatments
Snyder RJ, Bohn G, Hanft J, Harkless L, Kim P, Lavery L, Schultz G, Wolcott R
Wounds29pS1-S17(2017 Jun)
44)<i>Staphylococcus aureus</i> biofilm removal by targeting biofilm-associated extracellular proteins.
Shukla SK, Rao TS
Indian J Med Res146pS1-S8(2017 Jul)
https://mpkb.org/home/pathogenesis/microbiota/biofilm

Herbal medicines are preparations made from plants or plants parts or whole extracts or concentrates of active plant constituencies. The preparations are available as fresh plant products and as solid or liquid dosage forms. Fresh plant products are usually prepared as an infusion (tea) by pouring water over the herb and getting to steep. A decoction is prepared by directly boiling the herb in water, then straining to remove excess plant material. The liquid forms include medicinal oils, medicinal spirits, plant juices, syrups, and tinctures. Solid dosage forms are available as powdered plant material powdered extracts and concentrate. Solid preparations include granules, tablets, capsules, and lozenges. Herbal medicines also are available as herbal combination products. Herbal medicines defined by the European Union as "medicinal products containing as active ingredients exclusively plant material and or vegetable drug preparations." From the historical perspective, herbal medicines have been used since the dawn of humanity. Herbal remedies are phytomedicines that contain plant material with pharmacologically active constituents and often contain inert constituents such as starch, colouring matter, and other substances that have no defined pharmacologic activity. The dried herbal or whole plant extract is considered the active ingredient. Thus, herbal remedies may contain single chemical substances or complex mixtures of compounds that can produce a wide range of pharmacological effects. The active constituencies are mostly secondary metabolites that are present in small concentrations in the plant. It is hypothesized that the plant produces these secondary compounds as protection against insects and parasites.the amount of chemical constituencies varies because of many factors, including a type of soil, sunlight, rain, time of the season of collection, temperature, the maturity of the plant, associated flora, and storage conditions. Many herbs contain chemical compounds that are structurally related and can produce similar pharmacological activity. Thus therapeutic effects are likely the result of combined or synergistic action rather than one single compound. The active constituencies are present in lower concentrations than in purified, single-compound synthetic pharmaceutics. Overall the risk associated with crude herbal remedies are much fewer than conventional drugs when administered in appropriate doses.

1. Stay active. It’s more important than ever to keep exercising. It’s been scientifically proven that moderate exercise on a regular basis boosts the immune system and minimizes the risk of illness. It’s also a big mood booster, which we all need right now. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095254618301005 2. Reduce your stress. Too much stress negatively impacts your immune system. One of the best immunity-boosting stress-management techniques is meditation. Learning to meditate is easy. 3. Ditch the alcohol. Drinking too much interferes with the immune system, and according to research, increases your vulnerability to illness, including pneumonia and other infections. Alcohol abuse also decreases your levels of T-cells, which are the body’s natural virus fighters, making it harder to fight off illnesses. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4590612/ 4. Get adequate sleep. Sleep deprivation lowers immune function, so make sleep a priority. This study exposed participants to the common cold virus and found that people who snooze 6 hours or less are 4 times more likely to get a cold than those who slept 7 hours or more. If you need help getting the rest you need, Restful Sleep includes natural ingredients and calming herbs to help promote sustained restorative sleep. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26118561/ 5. Power immunity with probiotics. Your gut health is tightly linked to how well your immune system functions. A study found that probiotics support healthy gut bacteria and enhance immune function. To promote gut health, eat fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi or kefir. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25311611/ 6. Optimize your vitamin D level. Having a vitamin D deficiency increases your susceptibility for infections, according to this scientific report.What’s troubling is that approximately 75% of Americans have sub-optimal levels of this important immune boosting vitamin. Natural sources of vitamin D include sunshine (about 15 minutes outside can help) and supplementing with a high-quality nutraceutical like Vitamin D3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3166406/ 7. Eat more mushrooms. A growing body of research shows that some types of mushrooms contain immunostimulating properties. Add some shiitake or reishi mushrooms to soups, stew, or salads. And supplementing with a high-quality Chaga or Lion's Mane extract. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12436306/ 8. Zinc Zinc is needed for immune cell development and communication and plays an important role in inflammatory response. A deficiency in this nutrient significantly affects your immune system’s ability to function properly, resulting in an increased risk of infection and disease, including pneumonia https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27255474/ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19710611/ 9. Vitamin C This vitamin supports the function of various immune cells and enhances their ability to protect against infection. It’s also necessary for cellular death, which helps keep your immune system healthy by clearing out old cells and replacing them with new ones https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29099763/ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9374039/ 10. Elderberry Black elderberry (Sambucus nigra), which has long been used to treat infections, is being researched for its effects on immune health. Elderberry extract demonstrates potent antibacterial and antiviral potential against bacterial pathogens responsible for upper respiratory tract infections and strains of influenza virus. What’s more, it has been shown to enhance immune system response and may help shorten the duration and severity of colds, as well as reduce symptoms related to viral infections. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3056848/ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1756464619300313?via%3Dihub https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27023596/ 11. Selenium. Selenium is a mineral that’s essential for immune health. Animal research demonstrates that selenium supplements may enhance antiviral defense against influenza strains, including H1N1. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30593352/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4288282/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6165773/ 12. Licorice. Licorice contains many substances, including glycyrrhizin, that may help protect against viral infections. According to test-tube research, glycyrrhizin exhibits antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12814717/ 13. Echinacea. Echinacea is a genus of plants in the daisy family. Certain species have been shown to improve immune health and may have antiviral effects against several respiratory viruses, including respiratory syncytial virus and rhinoviruses https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4058675/ 14. Propolis. Propolis is a resin-like material produced by honeybees for use as a sealant in hives. Though it has impressive immune-enhancing effects and may have antiviral properties as well. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6335834/

In today’s day and age, the healthcare industry throughout the globe likes to push the idea that pharmaceuticals and medicinal remedies are the only options that we have when it comes to curing diseases, relieving symptoms, and boosting our health. And in some cases, the industry has even gone to great lengths to discredit naturally-derived medicinal products. However, in the world of alternative medicine, we very well know that for every human illness, there’s a natural plant standing by to offer some form of treatment. Today, we invite you into the Core Integrative Health mindset to learn just a bit more about alternative medicine, in addition to the natural plants found out in the world that can provide a world of benefits across a wide range of health issues, diseases, and complications. Most commonly, these various forms of alternative medicine come from natural herbs. Herbs That Carry A Power Now, if you’re new to the world of alternative medicine, fear not! This fantastic guide from the University of Rochester Medical Center offers an expert Guide To Common Medicinal Herbs to help you get started. Feel free to dive right into the guide yourself, or let us walk you through some of our favourite common herbs down below. Chamomile If you’ve heard of the word Chamomile, you’ve most likely seen it included into some tea blend, right? Typically, Chamomile tea is designed as a calming, relaxing type of tea that you’d drink before bed. And in fact, there’s tons of truth behind that! Chamomile has been used for centuries throughout the world for wound healing and to reduce swelling and inflammation. In addition, it’s been used as a sedative for anxiety and relaxation – making it one of our favourite natural herbs that offers a treatment for a wide range of health issues. Ginger Ginger root is another herb that many use for a number of gastrointestinal issues, as well as to treat nausea and even motion sickness. There’s a reason for why ginger ale is recommended for an upset stomach – although the sugar found in these soft drinks can do more harm than good. Natural ginger is always the way to go. Garlic Who doesn’t love the sweet smell of garlic in a fry pan? While you may not know it, garlic is actually one of the most important natural herbs that you could ever use as a form of alternative medicine. Typically, garlic is used to help lower cholesterol and blood pressure. In addition, it also has antimicrobial effects that help to protect your body from harmful microbes. Ginseng Have you ever drank ginseng tea? The chances are high that you have! Interestingly enough, ginseng has been considered as a “cure-all” for centuries – although research is still inconclusive of this claim. It is often used as a tonic and as an aphrodisiac.

Everyone loves a scoop of ice cream or a delicate cake to accompany their tea and celebrations, which is why so many people are unaware of the negative side effects of sugar today. We think to ourselves – sugar is just a sweet, innocent delicacy we can enjoy in small amounts throughout the day, right? Sure it must be harmless!

The medical community widely recognizes acute Lyme disease, but there is a great deal of debate over the existence of chronic Lyme, also known as post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome. Some researchers have suggested that chronic Lyme does not exist. This may be because patients who are treated with high-dose antibiotics for Lyme do not recover. Generally speaking, mainstream medicine assumes that if an infectious agent causes a disease, a patient should be at least cured, if not helped, by an antibiotic. Therefore, the very existence of the condition is questioned. The fact that many so-called chronic Lyme patients test negative for Borrelia does not help either. Many who acknowledge its existence have argued that chronic Lyme disease is caused by a single pathogen, Borrelia. The condition is caused by a community of microbes, one of which includes Borrelia. Borrelia is one of an increasing number of microbes documented to slow activity of the Vitamin D Receptor, undoubtedly in order to gain a survival advantage. It is for this reason that is merely targeting Borrelia is not sufficient to recover from Lyme. To recover, patients need to activate the immune response to target a range of pathogens. Clearly chronic Lyme patients are sick (and not with a mental condition), but this does not necessarily support the use of high-dose antibiotics, mainly since the drugs are demonstrably ineffective. High-dose antibiotics are highly immunosuppressive, doing nothing to attack the pathogens responsible for chronic disease. Dr Lorecki's Protocol is an attempt to do the opposite. Rather than use immunosuppression, Dr Lorecki wants to modulate the immune system.

The Prime Cause and Prevention of Cancer Dr Otto Warburg Lecture delivered to Nobel Laureates on June 30, 1966 at Lindau, Lake Constance, Germany " There are prime and secondary causes of diseases. For example, the prime cause of the plague is the plague bacillus, but secondary causes of the plague are filth, rats, and the fleas that transfer the plague bacillus from rats to man. By the prime cause of a disease, I mean one that is found in every case of the disease. Cancer, above all other diseases, has countless secondary causes. Almost anything can cause cancer. But, even for cancer, there is only one prime cause. The prime cause of cancer is the replacement of the respiration of oxygen (oxidation of sugar) in normal body cells by fermentation of sugar. All normal body cells meet their energy needs by respiration of oxygen, whereas cancer cells meet their energy needs in great part by fermentation. All normal body cells are thus obligate aerobes, whereas all cancer cells are partial anaerobes. From the standpoint of the physics and chemistry of life, this difference between normal and cancer cells is so great that one can scarcely picture a greater difference. Oxygen gas, the donor of energy in plants and animals, is dethroned in the cancer cells and replaced by the energy-yielding reaction of the lowest living forms, namely the fermentation of sugar. In every case, during the cancer development, the oxygen respiration always falls, fermentation appears, and the highly differentiated cells are transformed into fermenting anaerobes, which have lost all their body functions and retain only the now useless property of growth and replication. Thus, when respiration disappears, life does not disappear, but the meaning of life disappears, and what remains are growing machines that destroy the body in which they grow. All carcinogens impair respiration directly or indirectly by deranging capillary circulation, a statement that is proven by the fact that no cancer cell exists without exhibiting impaired respiration. Of course, respiration cannot be repaired if it is impaired at the same time by a carcinogen. To prevent cancer it is therefore proposed first to keep the speed of the bloodstream so high that the venous blood still contains sufficient oxygen; second, to keep high the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood; third, to add always to the food, even of healthy people, the active groups of the respiratory enzymes; and to increase the doses of these groups, if a precancerous state has already developed. If at the same time exogenous carcinogens are excluded rigorously, then much of the endogenous cancer may be prevented today. These proposals are in no way utopian. On the contrary, they may be realized by everybody, everywhere, at any hour. Unlike the prevention of many other diseases, the prevention of cancer requires no government help, and not much money. Many experts agree that one could prevent about 80% of all cancers in man, if one could keep away the known carcinogens from the normal body cells. But how can the remaining 20%, the so-called spontaneous cancers, be prevented? It is indisputable that all cancer could be prevented if the respiration of body cells were kept intact. Nobody today can say that one does not know what the prime cause of cancer is. On the contrary, there is no disease whose prime cause is better known, so that today, ignorance is no longer an excuse for avoiding measures for prevention. That the prevention of cancer will come, there is no doubt. But how long prevention will be avoided depends on how long the prophets of agnosticism will succeed in inhibiting the application of scientific knowledge in the cancer field. In the meantime, millions of men and women must die of cancer unnecessarily. "

Brace Yourself! Flu Season Is Coming Do You Have Everything You Need To Protect Your Body This Flu Season? Let’s face it, flu season is almost upon us, which means that local pharmacies, doctors offices, clinics, and walk-ins are going to be flooded with children, adults, and seniors looking to receive their annual flu shot to help keep them protected against this years’ strains. And while many swear on this type of vaccination and preventative care, a large swath of the population opt for a more natural, more holistic, and less invasive immune system boost specifically designed to give your body what it needs to defend itself against the flu. Let’s take a look at some of the various ways that herbal medicine and natural alternative health remedies can keep your body protected against the flu this winter. Boost Your Immune System With A Comprehensive Flu Defense If you’re looking to prevent the flu this year without having to go through an invasive vaccination, then it may be time for you to look into an alternative flu defence specifically designed to leverage the power of natural herbs and give your body the immune system boost that it needs. Herbal Teas Did you know that there are hundreds of herbal teas specifically designed to give your immune system a valuable boost? Not only do these herbal teas help to protect your body from the flu, but they also help to protect your body from more common seasonal illnesses like a winter cold, a cough, and even sinus infections. Herbal Tinctures Tinctures are quickly becoming a popular option when it comes to herbal remedies because they come in a highly concentrated liquid form. In this form, users can easily and quickly administer their herbal extract directly into their mouth with a dropper, and they can even administer a few drops in their favourite tea or beverage. Herbal Syrups Herbal syrups are another popular option for those who seek a flavoured herbal remedy that they can integrate into their diet. Herbal syrups come from a variety of different natural plants and offer a high-potency extract that provides your body with the support it needs to maintain a strong, healthy immune system. Homeopathic Remedies Those who believe in homeopathic remedies believe that the body has the ability to cure and heal itself when it’s given the proper resources to do so. These resources include small amounts of specific plants, natural herbs, minerals, and other types of natural substances that can be found in the world around us. These types of remedies are popular amongst those who want to be sure that they fuel their body with safe, natural, and non-artificial remedies to support their health. Are You Protected For Flu Season? After reviewing the various herbal remedies that you can use to keep yourself safe from the flu this season, do you feel prepared to face flue season head-on? If you’re ready to learn more about alternative medicine and natural herbs, visit Core Integrative Health today.

What is bee pollen? Bee pollen, also known as ambrosia, is simply pollen packed together by honeybees to form pellets. When honey and bee secretions are added to bee pollen, it is referred to as bee bread. Bee bread is stored in brood cells of combs and acts as a major food source for young bees. For honeybees, making bee pollen is a rather long and intricate process necessary to ensure the survival of the colony. In order to make bee pollen, worker bees must first collect a substantial quantity of pollen grains. Once a worker bee lands on a flower, it initiates the harvesting procedure by scraping the loosely attached pollen off the anthers of the flower and moistening the pollen with a dash of honey that it brought from the hive. It does this using its front limbs and mandibles. The bee also uses pollen combs (enlarged tarsal segments covered with thick bristles) located on its legs, to brush off excess pollen from its body. By skillfully contracting its auricles, the worker bee is able to push the collected pollen grains into its pollen baskets (concave regions surrounded by a fringe of long hairs) located on the outside of its tibias. The worker bee will continue doing this until its baskets are fully loaded. When the pollen baskets are filled up, the microscopic pollen grains will be compressed into a single granule known as bee pollen. An interesting fact about bee pollen is that it cannot be perfectly re-engineered in a laboratory. Several chemical analyses have been conducted on natural bee pollen using state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment, but scientists have still not been able to identify some of the compounds present in bee pollen. When bees are fed bee pollen that has been synthesised in a lab environment, they die even though the bee pollen is nutritionally similar to natural bee pollen. As a result, researchers predict that bees add additional unknown compounds into bee pollen during its formation. These unidentifiable compounds may very well be the reason behind the medical marvels exhibited by bee pollen. Another fascinating fact about bee pollen is that it takes a single bee, working eight hours a day, for an entire month to collect one teaspoon of bee pollen. Each teaspoon of bee pollen contains over 2 billion pollen grains. A single grain of bee pollen contains more than two million pollen grains. Bee Pollen Uses Bee pollen has all of the nutritional components necessary for sustaining life. The levels of essential elements present in bee pollen are remarkably higher compared to wheat germ and brewer’s yeast. Bee pollen has been scientifically proven to correct various nutritional deficiencies plaguing our present-day societies that consume nutritionally incomplete foods, often loaded with toxic chemicals. Many cultures throughout the world use bee pollen for various purposes. Some of the common uses of bee pollen include: Preventing mild communicable diseases, such as the common cold Helping overcome mental retardation and other developmental problems in children Improving endurance and vitality Aiding recovery from chronic illness Weight gain during rehabilitation and recovery Curbing cravings and addictions Anti-cancer properties Bee Pollen Benefits Bee pollen is a nutritionally complete food source. It contains many nutritional elements that lack in animal products like meat, eggs and milk. Bee pollen has a higher protein percentage than any animal product of equal weight. Several medical reports have shown that bee pollen is nutritionally superior to common foods being consumed today. One such report by researchers at the Institute of Apiculture in Taranov, Russia states that bee pollen is the most nutrient-dense natural food known to man. It has incredibly high levels of vitamins, minerals, free amino acids, nucleic RNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). Bee pollen also contains high levels of rutin – a vital nutritional element responsible for maintaining healthy blood vessels. Health concerns related to nutritional deficiencies are on the rise worldwide. Since bee pollen contains most of the essential nutrients needed by humans, it is utilised on a large scale as a nutritional supplement to combat various nutrient deficiencies. Improved Physical Abilities Many renowned naturalists and athletic coaches have attested to the wonderful benefits offered by bee pollen to athletes. The British Sports Council conducted research on the effects of bee pollen on the strength levels of athletes. The findings of the study showed a 40-50 per cent increase in strength in the athletes taking bee pollen regularly. More astounding revelations came from the British Royal Society, which reported height increases in adults who consume bee pollen regularly. Antii Lananaki, the coach of the Finnish track team that dominated the 1972 Summer Olympics held in Munich, West Germany commented that most of their athletes take bee pollen food supplements. Studies that they conducted on bee pollen indicate that it considerably boosts physical performance. He also added that none of their patients experienced any negative effects from taking bee pollen. The late Alex Woodly, a coach/mentor for many Olympic gold-medal sprinters in the 1960’s-1970’s and a former head of the prestigious Philadelphia Pioneer Club was a true believer in the great benefits of bee pollen for athletes. He once said that bee pollen increases the strength and endurance of athletes by 25 percent with zero side effects. Unlike steroids and other artificial chemical substances that some athletes these days pump into their system, bee pollen is as natural as it gets- a true gift of vitality from Mother Nature. Just like Woodly, famous German naturalist Francis Huber was a great proponent of the nutritive benefits of bee pollen. Huber used to refer to bee pollen as “The greatest body-builder on Earth.” Immune Booster According to a report entitled, “Comparative Studies Concerning Biochemical Characteristics of Beebread as Related to the Pollen Preserved in Honey”, bee pollen supplementation significantly enhances immune function. This report outlines the findings of research conducted by Dr E. Palos, Z. Voiculescu, and C. Andrei of the Agronomic Institute, Faculty of Zootechnics Romania. The results of the research are as follows: Bee pollen supplementation was found to significantly increase the level of blood lymphocytes, gamma globulins and proteins. Lymphocytes, also known as white blood cells act as the immune system’s “fighters”. Apart from being the body’s first line of defence against disease-causing microbes, white blood cells also perform other duties like ridding the body of old, infected, mutated or cancerous cells and metabolic wastes. Gamma globulin is a protein synthesised in the blood. It plays a critical role in the body’s ability to ward off infection. Antibiotic Properties To date, experiments conducted on bee pollen have established that bee pollen has antibiotic properties that will inhibit the growth of some bacteria. These studies have specifically indicated that bee pollen is very effective against strains of salmonella and several other disease-causing agents. Regulates Intestinal Function Clinical studies have shown that bee pollen has a regulatory effect on intestinal function. This effect can be attributed to its high levels of cellulose and fibre, as well as the existence of antibiotic factors. Balances Cholesterol Researchers have reported that bee pollen has the ability to restore normal cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the body. When incorporated into the diet, bee pollen has been shown to increase the levels of high-density lipoproteins (HDL), while decreasing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels. Stabilisation of blood serum cholesterol levels has also been observed. Treats Cancer “Delay in the Appearance of Palpable Mammary Tumours in C3H Mice Following the Ingestion of Pollinated Food”, a research article written by William Robinson, Ph.D. and published by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (NCI) in October 1948 suggests that bee pollen can actually be used in the treatment of cancer, specifically breast cancer. In the article, Dr. Robinson clearly outlines all the experiments he carried out. The mice used in the research were bred in such a way that they would develop and subsequently die from mammary tumours. The age at which these mice developed tumours was between 18 to 57 weeks with an average appearance at 33 weeks. Tumour incidence in this strain of mice was 100%. The mice were divided into two groups; one group was fed only normal mice food, while the other group was fed mice food mixed with bee pollen in the ratio of 1 part bee pollen to 10,000 parts food. Since low body weight can delay the development of tumours, keen attention was paid to the weight of the mice. The mice being fed pollinated food registered no decrease in weight. Instead, they actually showed a slight increase in weight, possibly due to the nutritional factor in bee pollen. The results of Dr Robinson were as follows: The group of mice that were fed normal mice food developed mammary tumours as anticipated- at an average age of 31.3 weeks, while the group of mice that was fed pollinated food exhibited delayed mammary tumour development- at an average age of 41.1 weeks. Moreover, seven mice in this group still remained tumour-free at 56-62 weeks of age, when the experiments were terminated. Considering the fact that breast cancer is the second most common, newly-diagnosed cancer and second leading cause of cancer deaths among women in the United States, one would think that people would take this article seriously. Yet, the exact opposite of this has occurred. The scientific society has not even bothered to follow up on this promising line of research. Unfortunately, the National Cancer Institute has also simply discarded Dr. Robinson’s findings without any explanations. More promising findings came from the University of Vienna, where Dr. Peter Hernuss, along with other researchers, carried out a study involving 25 women suffering from inoperable uterine cancer. All the women were treated with chemotherapy since surgery was not an option. Some of these women were given bee pollen with their food, while others were given plain food without bee pollen. The women who received bee pollen supplementation rapidly exhibited an improvement in immune function, marked by increased levels of cancer-fighting cells. In addition to this, these women suffered less from the awful side effects of chemotherapy, such as nausea, insomnia and hair loss. The group of women who were not given bee pollen exhibited no comparable improvements. Treatment of Infertility Problems Bee pollen supplementation has been found to improve ovarian function in women suffering from infertility significantly. In women receiving bee pollen supplementation, an increased intensity of ovulation along with the ability of the ova to withstand the incubation period is observed in respect to the placebo group. For the best results, it is recommended for women to supplement with bee pollen in the ratio 2 parts per 100 of pollen and with the substitution of animal proteins with pollen in a proportion of 5 parts per 100. Treatment of Anemia Various studies involving lab animals have proven the effectiveness of bee pollen when it comes to treating anaemia. The ingestion of bee pollen by anaemic patients has been shown to considerably increase their levels of haemoglobin (the iron-rich oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells). A significant increase in both lymphocytes (white blood cells) and erythrocytes (red blood cells) levels has also been observed in the patients. Weight Control Whenever the subject of weight control is brought up, many people tend to focus on weight loss rather than weight gain. This is probably because of the numerous health problems associated with being overweight. However, being underweight can still be as detrimental as being overweight. Just like there is a healthy maximum weight limit, there is also a healthy minimum weight limit. Some of the health issues associated with being underweight include; inhibited growth and development (especially in children and teens that are still actively growing), fragile bones, weakened immune system, anaemia, fertility issues and hair loss. So, how can one stay within the confines of a healthy weight limit? For one, incorporating a healthy diet into your daily regimen is a good way to start. With a diet consisting of all the macro and micronutrients in their appropriate amounts, both weight gain and weight loss are pretty much achievable. But, does such a diet exist? Why, of course, it does. However, such a diet can be pretty expensive for most people and rather cumbersome to maintain. The only cost-effective and straightforward alternative comes through the use of bee pollen. This food works miracles when it comes to weight-stabilisation or weight-control. In weight-loss programs, bee pollen activates the metabolic processes responsible for speeding up the caloric burn in the body. Given that bee pollen is one of the most nutrient-dense foods in the world, and it contains only ninety calories per ounce, makes it an exceptional weight-loss food. Lecithins (which are phospholipids, composed of phosphoric acid with glycerol, choline or other fatty acids usually glycolipids or triglyceride) play an important role in the lowering of body fat percentage. Since lecithin is a natural fat emulsifier, consuming more of it can inhibit fat storage. Bee pollen contains about 15% lecithin by volume. This makes it the perfect “fat burner.” Bee pollen contains significant amounts of the essential amino acid L-Phenylalanine, which is a known appetite suppressant. L-Phenylalanine works by stimulating the release of cholecystokinin- a gut hormone which signals the brain to slow down digestion creating sense satiety shortly after eating. Bee pollen also curbs cravings by filling in nutritional gaps that may exist in your diet. In a weight-gain program, bee pollen can be used as a nutritional supplement. According to several studies, an average bee pollen sample roughly contains 20% proteins, 25% carbohydrates, 5% fatty acids, and the remaining 50% is composed of minerals, fibre, vitamins, enzymes and water. Health and Beauty Beauty can be seen as directly correlated to health. Our health involves what we put in and on our bodies. After all, you are what you eat! Eating a healthy diet and using natural skin products will go a long way in determining how you look. In today’s weight-conscious society, having a beautiful face is not enough. Physique plays a significant role in your overall appearance. When bee pollen is included in the daily diet, it not only provides you with essential nutrients to keep your skin healthy and radiant, but it also aids in safe weight control. Bee pollen can also be blended with other natural ingredients to make relatively inexpensive body lotions and creams for adding that extra touch of radiance to every inch of the outside of your body. Dr. Lars-Erik Essen, a renowned dermatologist from Helsingborg, Sweden and a pioneer in the field of bee pollen and skincare products, has successfully treated many of his patients suffering from various skin conditions using bee pollen skin products. Dr Essen argues that bee pollen exerts impressive effects on the skin via transcutaneous nutrition, primarily, because it contains a high concentration of RNA and DNA as well as antibiotic factors. Some of these effects include preventing premature ageing of skin cells, stimulation of blood flow to the skin, activating the growth of new skin tissue and protection against dehydration. All these positive effects make the skin become smoother, healthier and less prone to wrinkles. Two Russian scientists, Professors N. Mankovsky and D. G. Chebotarev, carried out research and proved that bee pollen stimulates skin cell renewal. The two scientists asserted that the rejuvenation of skin and body cells could be encouraged by the interaction of the elements present in bee pollen such as microelements, poly-vitamins, enzymes, amino acids and hormones. The professors went on to refer to the properties of bee pollen as being vital to a form of internal and external rejuvenation at the cellular level. Allergy Treatment Over the ages, bee pollen has been used by many cultures as a remedy for allergies and hay fever. But, given the fact that pollen is a common allergen, many people would consider it foolish to use it as a remedy against allergies. Nonetheless, bee pollen still works! So, how does this golden dust work? To understand the concept behind the workings of bee pollen, it is imperative that we first know how immunisation works. This is because their working principles are more or less similar. During immunisation, an individual is given an attenuated (weakened) form of the disease-causing micro-organism to ‘trick’ the recipient’s immune system into thinking that the body is under attack. In response to this false alarm, the immune system will produce antibodies to counteract the infection. The immune system will then keep a memory of this attack enabling it to work quickly and more efficiently during future attacks by similar microbes. In the treatment of allergies using bee pollen, a technique similar to immunisation is used. This technique is known as desensitisation. Scholars developed desensitisation at St. Mary’s Hospital Medical School in London during the early 19th century. The treatment involves administering small doses of the allergen- which in this case is bee pollen- to the patient to elicit an immune response that will eliminate the allergic reaction. After the elimination of the allergic reaction, the immune system will record the attack and make more antibodies to counter a similar allergic response in the future. For the treatment to work, the patient must be repeatedly given small doses of the allergen over a certain period of time, usually not less than 6 weeks before the beginning of the season and throughout the season. Leo Conway MD., an early pioneer in the field of allergies from Denver, Colorado, treated his patients of various illnesses using bee pollen. Given that oral feeding of pollen for the treatment of multiple ailments was first perfected in his lab, astounding results were obtained. Dr. Conway reported that ninety-four percent of all his allergy patients were completely cured of their allergies. All the patients who had taken bee pollen for three years stayed allergy-free regardless of their lifestyles. Even the remaining six percent, most of who failed to follow the prescription correctly, exhibited some sense of well-being after the treatment. Dr Conway asserted that control had been achieved in 100 per cent of his previous cases and the field is ever-growing. He also added that no ill side effects were recorded from the uses of bee pollen. Some of the illnesses that Dr Conway has successfully treated include hay fever, ulcers of the digestive tract, pollen-induced asthma, bronchitis, sinusitis, colitis, migraine headaches and urinary tract disorders. Bee Pollen Dosage Appropriate bee pollen dosage will depend on various factors- the form of bee pollen you are planning on taking (capsules or granules), your reasons for taking bee pollen, your past experience using bee pollen, your medical history etc. If you are trying out bee pollen for the first time, it is always important to consult your doctor first. Most of the bee pollen sold in health stores will come with guidelines on how to use it. If you happen to buy bee pollen that has no direction on how it should be taken, you can always consult a local herbalist or the person who sold it to you. But, be careful who you ask for advice as some people may mislead you knowingly or unknowingly. The good news, however, is that there are no known Bee Pollen overdoses. Still, it is important to start small and work up to the amount that works for you as some people may be allergic to Bee Pollen. Recommended dosage: There is no scientifically proven dosage for Bee Pollen. Some people recommend anywhere from 500mg to 2000mg of Bee Pollen per day, but there is no proof of the effects this has. It is recommended you start with a low dosage and increase it based on how you feel.
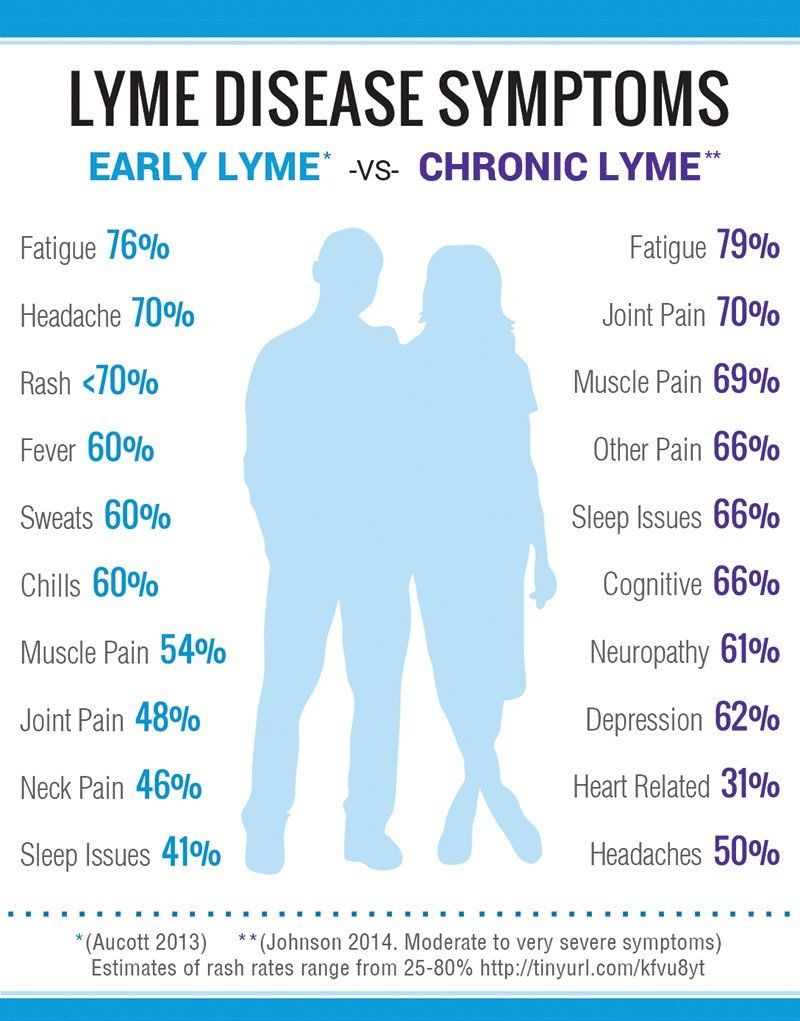
The latest scientific research has revealed that 90% of all the cells in your body are microbes. Another way of saying this is that there are 20 times more “bugs” in your body than there are of your cells. Our society has completely bought the concept that we get sick because of the presence of microbes, but is that the complete story, or even the true story? In cases of Lyme disease, for instance, it seems very self-evident in some cases that “I was bitten by a tick which regurgitated its stomach contents into the body which introduced Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria into your body…a bulls-eye rash developed around the bite site…and soon, many symptoms started showing up. This sounds plausible that the bacteria caused the illness. But does it explain everything? Not really. Consider that only about 40% of people ever develop a bulls-eye rash. Many people never were bitten at all. Many who test highly positive never have any symptoms…ever! How you act, and the physical symptoms you suffer from may have more to do with your ancestors than with your lifestyle. The theory of epigenetic miasms may explain some of what makes you uniquely prone to the types of problems you experience that are collectively called Lyme disease. This is not “new age”, nor are we talking about genetic mutations, but it is more of an epigenetic phenomenon. An Epigenetic miasm, by definition, is a predisposition, or tendency, of certain psychological and physical problems that are set in motion by illnesses in your family history going back seven generations, or acquired within your lifetime. Epigenetic miasms are due to changes in the expression in genes that are not due to underlying changes in the actual DNA sequences. Epigenetic miasms are not to be confused with genetic abnormalities, such as missing or mutated genes. Epigenetic miasms are more of an energetic and epigenetic abnormality. John Davidson, a researcher and author on bio-energetics, states that “Miasms are essentially an energy disharmony, disease pattern or imbalance.” Scientific research dating back over 200 years documents the reality of these epigenetic problems, though the term epigenetics was only coined recently when researchers on the Human Genome Project realized that instead of the expected 200,000+ gene sequences they only found humans have only 25,000. What this means is anyone who is expecting genetic engineers to be able to come up with a cure for every illness can stop waiting. The problems are not to be found in incorrect sequences of genes in most situations. Therefore the term "epigenetics" was coined to explain the energetic phenomenon that expresses through the DNA as opposed to the actual DNA structure be the end all cause of illness. Epigenetic miasms are usually started by improperly treated illnesses that can go back as far as seven generations of your family tree. In other words, some of the tendencies to problems you have could be the result of illnesses or medications experienced by your great, great, great…grandparents. For over two hundred years, scientists have been tracking the epigenetic miasms caused by specific illnesses. Today we have immense collections of data outlining what kinds of problems future generations may experience due to different illnesses. Gonorrhoea, syphilis, tuberculosis, cancer, and many more, all will generate a specific set of problems unique to the illness when suppressive therapies are used to treat them. Homeopathic texts have pages of symptoms of the body and mind, which are completely predictable in a miasmatically affected family line for each type of miasm. Antibiotics are a suppressive therapy and the major culprit to creating epigenetic miasms. The antibiotics do kill most of the bacteria that cause these different illnesses, but they do nothing to address the damage already done by the bacteria on a physical and bio-electrical level in the patient’s body. For example, if you find that you have termites in your house, you can call an exterminator to come out and kill the termites. By killing the termites, you have eliminated any worsening of the problem; however, you have done nothing to correct the myriad of tunnels through the woodwork of your house. To make matters worse, you now have a very toxic chemical insecticide in your house. The energetic (epigenetic) tunnels and toxins in the body, in a nutshell, are what cause epigenetic miasm to occur. It can also be likened to using a computer that is infected with a computer virus to build new computers. The new computers will be similarly affected. Epigenetic miasms are very much like a computer virus in your body's operating system. It doesn't kill you outright. It only corrupts various aspects of your body's operating systems when activated by certain stressors in your life. Epigenetic miasms predispose you to react to the tick bite and developing the myriad of symptoms we call Lyme disease. It is very obvious that the bacteria affect the areas of the body, which were epigenetically weakest first, and then as more body systems become compromised, they move in and cause even more symptoms. The point that is clear is that if the underlying epigenetic flaws are addressed in advance or even after the initial bite, and the overall coherence of the body is restored, and the microbial load is reduced, then we would see a gradual disappearance of symptoms. One of the primary reasons to be treated for epigenetic miasms in young people is to avoid passing on to their offspring, the epigenetic flaws that were associated with having had Lyme disease. The following is a list of known epigenetic miasm tendencies or predispositions from two major categories related to Lyme disease. Antibiotic-Induced epigenetic flaws and Syphilis epigenetic flaws (a very close relative of the Lyme spirochete). Remember, a person may never manifest any of these tendencies unless their life is unbalanced in some way. Antibiotic-Induced Epigenetic Predispositions: Friends to the world, very charismatic, but hardest on the ones they love the most. Emotional abuse, psychological warfare, never physically abusive. Wild feeling, abrupt, impulsive. Get better if left alone. Say they are sorry a lot because they recognize when they are wrong but are somewhat helpless to stop the anger once initiated. Night people. Get happier the later it gets, and most symptoms are worse in the morning getting better in the evening. Grumpy/irritable in the morning, generally like a darkened room over bright sunshine in the morning. Melancholy, sad, dismal outlook, but hurried and anxious High sex drive Prone to morning mucus but clears as the day goes on. Prone to low back pain and rheumatic aches and pains. Nocturnal bedwetting. Craves oranges, ice, very thirsty Ravenous appetite, hunger soon after eating Heels and ball of the feet tender Burning of the hands and feet. Asthma, diabetes, ovarian pain, shoulder pain, sciatica, warts, headaches, liver abscess, pelvic cellulitis, vertigo The sensation of a cavity where the heart ought to be Syphilis/Lyme Epigenetic Predispositions: Mindset: Hopeless and despairs of recovery Antisocial and apathetic Fears the night all symptoms worse at night Fears the suffering from physical and mental exhaustion upon awakening… utter prostration and debility in the morning Pains from darkness to light Very nervous laughs/weep without cause Feels as if going insane or being paralyzed Family history and predisposition to alcoholism Impulse to wash hands Profound Insomnia with great restlessness at night Restless Leg Syndrome… impossible to keep the legs in one position Excessive saliva which runs out of the mouth when sleeping Vomiting/nausea, chronic for weeks or months Heartburn with pain and rawness of the stomach Stupefying Headaches…deep crushing pains across temples. Hair Loss Asthma and coughing, worse sunset to sunrise. Chilly but sweats at night with exhaustion. Pain in the back in the kidney region, worse after urinating Chronic tooth decay The items on these lists are by no means complete. They simply give you an idea of what symptoms may be seen in a predisposed individual that gets bitten by a tick and is treated with antibiotics and who has a family history of Syphilis and antibiotic usage for any reason. In this world of antibacterial soaps, cleaners, and prescription antibiotics, you can see that the “Germ Theory” is alive and well in America. But are they truly the “cause of your illness”? What I have told you so far undoubtedly sounds totally contrary to everything you thought you knew about germs and infectious disease. Germs are not the cause of illness; they initiate the reaction in a predisposed individual. An analogy presented by Dr Otto Wolf, M.D., likens infectious disease to that of an explosion. Dr Wolf says, “The spark is the not cause of the explosion, it merely initiates the explosive potential of the dynamite. In this analogy, the spark is the bacteria, which initiates the disease potential of the individual.” Husemann F. and Wolf O., The Anthroposophical Approach to Medicine, Vol III. 1989 If your body has no “explosive potential” then bacteria cannot “ignite” an infectious disease. No one who is not predisposed through imbalance/dysfunction can ever develop an infectious disease. At this point, we need to clarify a very important point; there is a big difference between “infection” and “infectious disease”. Infection is a component of the tissue of the body, while the infectious disease is a factor of the human organism. Letterer, Die Medizinische (1953) In other words, infection merely means that you have a microbe in the tissues of the body…quite an understatement when considering 90% of what you think is you is actually them (microbes). The integrity of the human organism dictates whether or not that infection proceeds to cause the symptoms of infectious disease. You may have a potentially lethal microbe in the tissues and never manifest any disease because of it. However, once an infectious disease is initiated, it will take a course independent of the type of microbe. F. Horing, Klinische Infedtionslehre, 3rd ed. (Berlin: 1962) Its course is dictated by the host’s ability to adapt instantly and correctly to any changes in its internal and external environment, as well as the epigenetic miasms that are altering the person’s adaptability. This is why 600 thousand people can have the same type of bacterial infection and yet have totally different symptoms. With the Human Genome Project only being completed in recent years, very few doctors have even heard of epigenetic miasms and still fewer are trained in dealing with them. It requires special knowledge in recognizing the many types of miasms that may be present in a patient. These epigenetic miasms cannot be treated until a level of integrity and coherence is achieved in the patient, and their case is somewhat stabilized. Epigenetic miasms are a bio-energetic flaw in the “software” bio-communication/bio-regulation systems of the body, and therefore there is no “hardware” solution in the pharmaceutical realm.